What is the Internet?
Each question in this blog will be followed by a more specific question, and we won't stop until we dig out the truth.
What is the Internet?
The internet is a system architecture that has revolutionized communications and methods of commerce by allowing various computer networks around the world to interconnect. [2]
There are many connections that can be used for internet access. All these internet connections have their own speed range that can be used for different purposes like for home, or for personal use. [3]
What is the difference between "Network" and "Internet"?
The term "network" refers to a collection of two or more computer systems. It is a collection of computer systems and devices that are linked together utilizing LAN, WAN, CAN, or HAN.
The "internet" is the interconnection of a few networks. It is a global system that connects various sorts of electric devices worldwide.
What are the different types of computer network (check pictures below)?
PAN (Personal Area Network): a computer network formed around a person
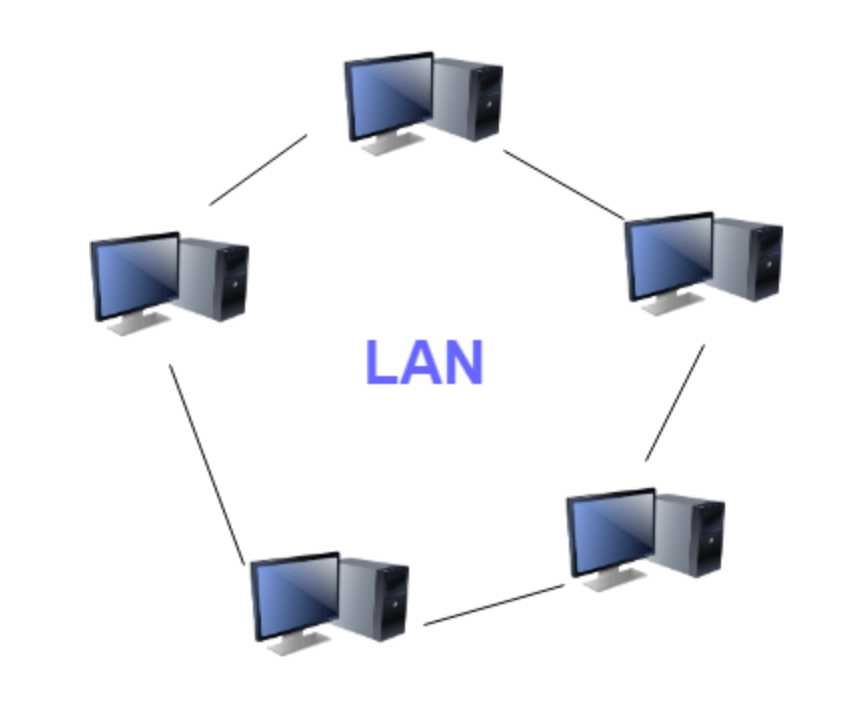
LAN (Local Area Network): a group of computer and peripheral devices which are connected in a limited area (such as school, laborator, home, and office building) that consists of less than 5000 interconnected devices across several buildings
WAN (Wide Area Network): a connection of a LAN which connects with other LANs using telephone lines and radio waves
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): a computer network across an entire city, college campus, or a small region in a maximum of 50km range
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network), same thing as WiFi: links single or multiple devices using wireless communication within a limited area like home, school, or office building [20]
SAN (Storage Area Network): allows consolidated, block-level data storage
System Area Network: offers high-speed connection in server-to-server and processor-to-processor applications for local networks
POLAN (Passive Optical LAN): a networking technology which helps you to integrate into structured cabling
Home Area Network (HAN): built using two or more interconnected computers to form a local area network (LAN) within the home
Enterprise Private Network (EPN): build and owned by businesses that want to securely connect various locations
Campus Area Network (CAN): made up of an interconnection of LANs in a specific geographical area
Virtual Private Network (VPN): a way to simulate a private network over a public network, such as the Internet [13]
What are the different types of internet connection (check pictures below)?
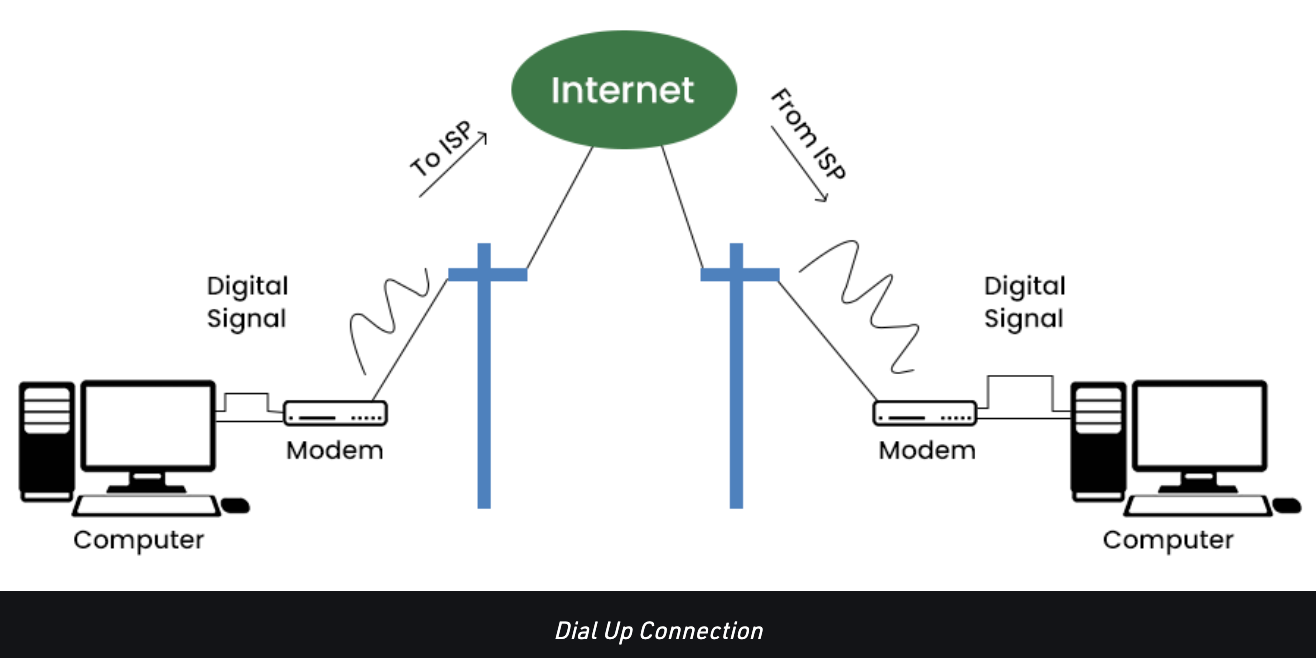
Dial-up connection: established between your computer and the ISP server using a modem
Broadband connection (How many types of broadband connection are there? Check the next next question!): refers to high-speed internet access that is faster than traditional dial-up access
Cellular: provides wireless Internet access through cell phones
Integrated service digital network (ISDN): a circuit-switched telephone network system
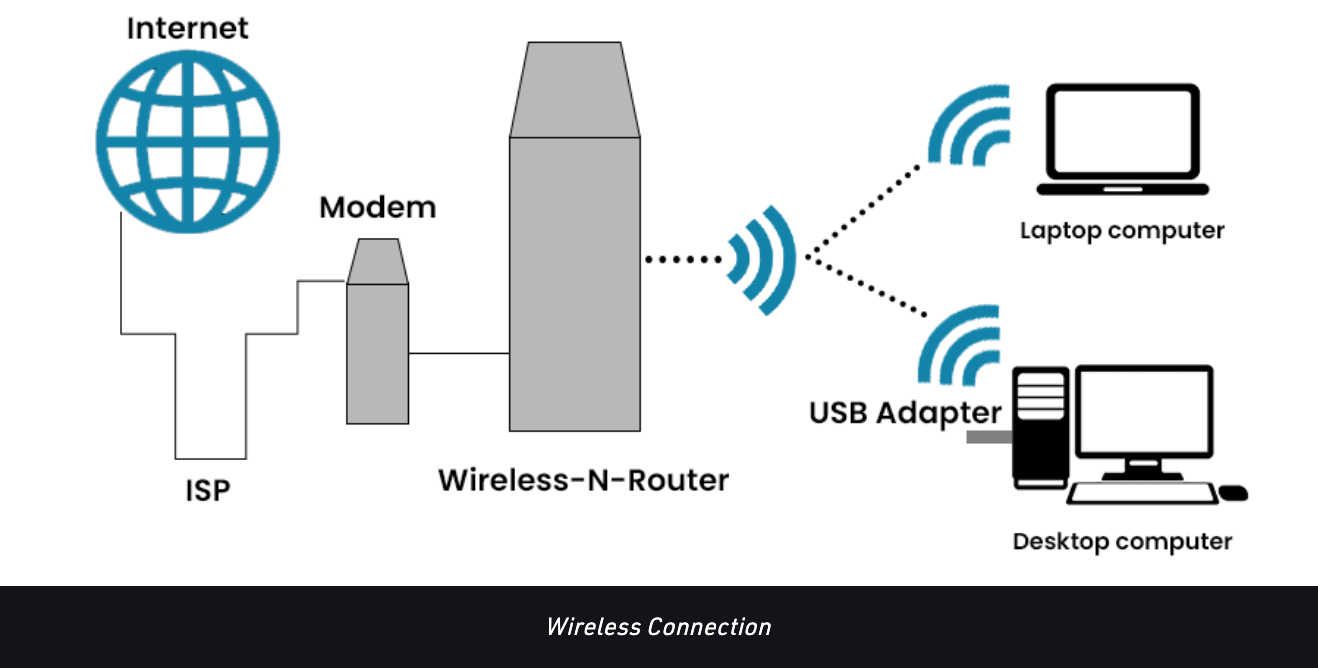
What are modems and routers (from the pictures above & below)?
A modem 调制解调器 uses a wide-area network (WAN) to bring the internet into the home.
A router 路由器 generates a local area network (LAN) to bring the internet to a collection of devices.
Both of these devices can incorporate the use of WiFi, which is a type of wireless technology. It is used by WiFi capable devices to connect to the internet via the wireless router.
What is an ISP (from the pictures above & below)?
An internet service provider (ISP) is simply a company (e.g. Verizon) that provides its customers with access to the internet [14].
What are the different types of broadband internet connection (check pictures below)?
Fiber optic: carry lots of data using pulses of light through strands of fiber at the fastest speeds
Wireless broadband (Wi-Fi): connects a home or business to the internet using radio signals instead of cables
Digital subscriber line (DSL): transmits data over traditional copper phone lines
Cable (e.g. Ethernet): high-speed internet that uses existing cable TV infrastructure
Satellite: uses communication satellites to transfer data
What does "broadband" mean?
Broadband 宽带 is the transmission of wide bandwidth data over a high speed internet connection. [6]
What does "bandwith" mean?
The maximum amount of data transmitted over an internet connection in a given amount of time.
Bandwidth 频率范围/频带宽度/带宽 is often mistaken for internet speed when it's actually the volume of information that can be sent over a connection in a measured amount of time – calculated in megabits per second (Mbps). [6]
What is WiFi? And what is a WiFi Network?
WiFi, or "wireless fidelity" (defined under IEEE 802.11 standards) [6], is a networking technology that uses radio waves to allow high-speed data transfer over short distances. It allows local area networks (LANs) to operate without cables and wiring. [8]
A WiFi network is a type of wireless local-area network (WLAN). [9]
It is simply an internet connection that’s shared with multiple devices in a home or business via a wireless router. The router is connected directly to your internet modem and acts as a hub to broadcast the internet signal to all your Wi-Fi enabled devices. This gives you flexibility to stay connected to the internet as long as you’re within your network coverage area. [6]
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet (defined under IEEE 802.3 standards) is a type of communication protocol that connects computers within what’s called a “local area network (LAN)” and a “wide area network (WAN).” [10]
What is the difference between WiFi and Ethernet?
A WiFi connection transmits data via wireless signals, while an Ethernet connection transmits data over cable. While WiFi connection is more convenient to connect and use, Ethernet connection is faster in speed, more secure, and reliable. [11]
What is radio wave? And why is it essential to WiFi technology?
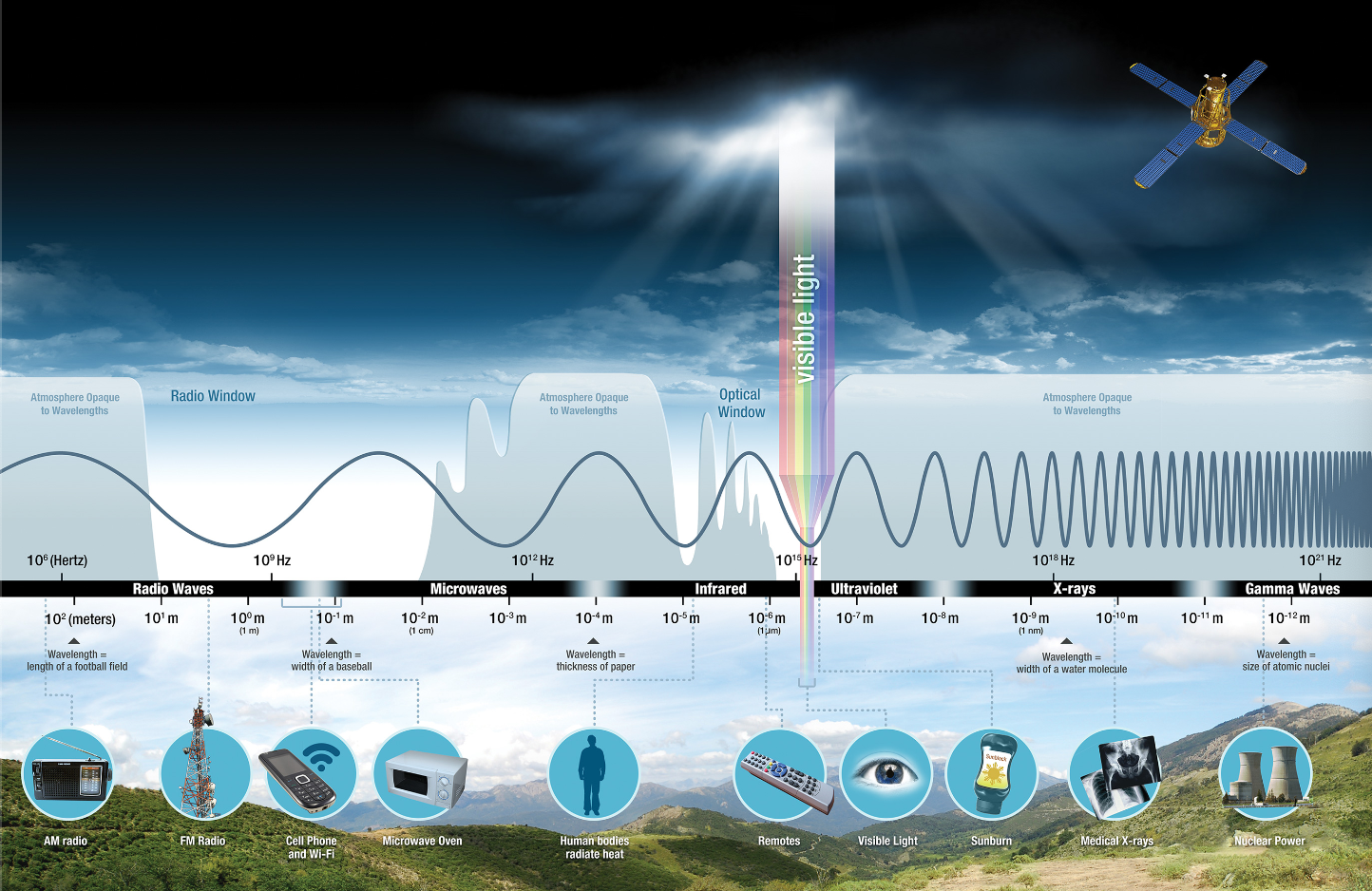
Radio waves, one of the 7 types of electromagnetic waves, have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum (check pictures below). They range from the length of a football to larger than our planet. Heinrich Hertz, a German physicist, applied Maxwell's theories to the production and reception of radio waves and proved the existence of radio waves in the late 1880s. [16] [17]
As mentioned before, Wi-Fi uses radio waves to transmit information between your device and a router via frequencies. Two radio-wave frequencies can be used, depending on the amount of data being sent: 2.4 gigahertz and 5 gigahertz. [19]
What is a hertz? It is just a measurement of frequency that is named after Heinrich Hertz. One hertz is a frequency of one wave per second. One megahertz is one million waves per second. One gigahertz is one billion waves per second. [19]
What is electromagnetic energy? What are electromagnetic waves?
The sun is our planet’s principal source of energy, and its energy travels in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic energy moves across empty space at the speed of light in the form of waves of electric and magnetic fields with a range of frequencies or wavelengths.
The terms light, electromagnetic waves, and radiation all refer to the same physical phenomenon: electromagnetic energy.
How to describe electromagnetic energy?
This energy can be described by frequency, wavelength, or energy.
All three are related mathematically such that if you know one, you can calculate the other two.
Radio and microwaves are usually described in terms of frequency (Hertz), infrared and visible light in terms of wavelength (meters), x-rays and gamma rays in terms of energy (electron volts).
This is a scientific convention that allows the convenient use of units that have numbers that are neither too large nor too small.
What is electromagnetic radiation?
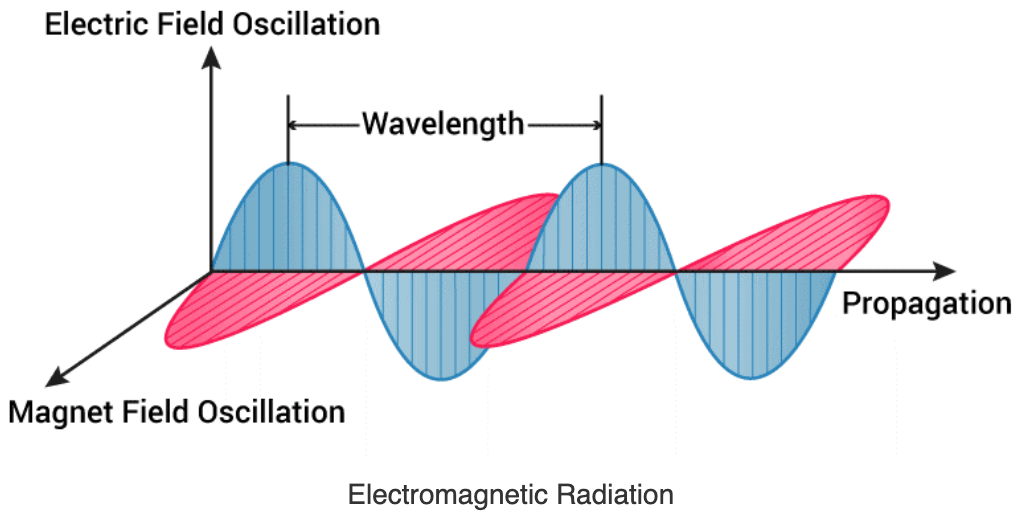
Electromagnetic radiation can be defined as a form of energy that is produced by the movement of electrically charged particles traveling through a matter or vacuum or by oscillating magnetic and electric disturbances.
The magnetic and the electric fields come at 90° to each other, and the combined waves move perpendicular to both electric and magnetic oscillating fields occurring during the disturbance.
What is "electric charge"? What is a particle? What are "electrically charged particles"? What is an atom?
All matter in the universe (anything that has substance) is made of small components called atoms. Every atom is made up of tiny elementary particles called electrons, protons, and neutrons. Electrons repel other electrons, but are attracted to protons. Protons repel one another, but are attracted to electrons. Neutrons neither attract or repel anything.
Generally, the number of electrons and the number of protons in an atom are equal to each other. When that happens, the atom is in a normal or neutral state.
An entire atom becomes electrically charged when the number of electrons or protons stops being equal. The "extra" electron or proton isn't balanced by something inside the atom anymore and begins to be attracted to the protons or electrons in other atoms.

Welcome to the world of atoms!
The goal of this post is to let anyone with or without technical background to fully understand the concept and fundamental principles of "internet". Then in the next few blog posts in the [Smart Home Series], we'll figure out the other components of smart home systems together.
Sources:
[3] GeeksForGeeks: Types of Internet Connection
[4] Difference Between Network and Internet
[7] Verizon's Broadband Definition
[9] Techtarget: What is the difference between WLAN and Wi-Fi?
[10] Techslang: What is Ethernet?
[11] Spectrum: What is the difference between wifi and ethernet?
[12] Different types of internet connections, speeds and affordability options
[13] Academia: Virtual Private Network
[14] Types of Internet Access Technologies, Explained
[15] GeeksForGeeks: Electromagnetic Spectrum
[16] NASA Science: Radio Waves
[17] NASA Science: Anatomy of an Electromagnetic Wave
[18] Science Sparks: What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
[19] Britannica: How does WiFi work?
[20] Scientific American: How does WiFi work?
[21] NASA Science: Introduction to the Electromagnetic Spectrum
[22] BYJU: Electromagnetic Radiation
[23] CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention): What is Radiation? The Electromagnetic Spectrum